Can Florida Charge More Than 6% Sales Tax When Registering A Car Out Of State
What is Value Added Tax (VAT)?
Value-added tax (VAT) is an indirect taxation which is charged at the time of consumption of goods and services and is levied when a value has been added over diverse stages of production/ distribution right from the purchase of raw materials till the final products are sold to the retail consumers.
The VAT is levied on the cost of the products at each stage, and its full brunt is borne simply past the final consumer since the producer of the production or supply chain distribution members tin take the credit of VAT paid past them. (i.east.) until the purchaser is not the end-user, the goods procured is the cost to the business organisation, and the tax paid on those purchases can exist reduced from the tax they charge on their customers.
Information technology is levied based according to the consumption of appurtenances and rather than the income of the consumers.
Calculation of Value Added Tax
VAT to be paid to Authorities = Output VAT – Input VAT
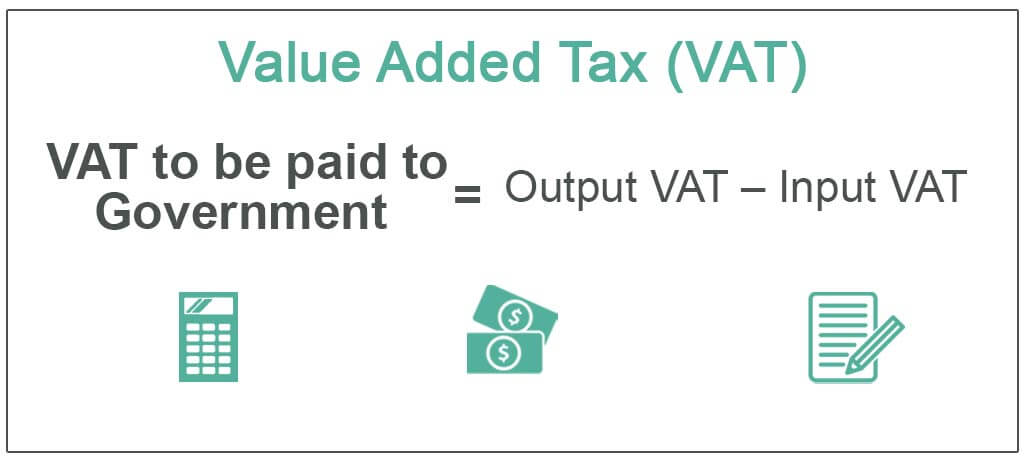
Y'all are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link Commodity Link to exist Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: Value Added Revenue enhancement (VAT) (wallstreetmojo.com)
- Output VAT = It is a tax charged on the sale of goods. It is charged on the selling price of the goods.
- Input VAT = It is the tax paid on the buy of goods. It is paid at the toll price of the goods.
Examples
Example #1
Theo is a chocolate manufactured and sold in the US. The Us has a x% Value added tax.
- Theo's Manufacturer procures the raw material at the cost of $10, plus VAT of $one – payable to the United states government. The total price paid is $eleven.
- The Manufacturer sells Theo to a retailer for $20 plus a VAT of $2 totals to $22. However, the Manufacturer pays but $1 to the U.s.a. government every bit that is the full VAT to be paid at this bespeak because the output VAT $two is reduced past the input VAT of $1 paid during the procurement of raw materials. $1 paid represents the VAT on value addition fabricated in the toll price of $10 ($twenty – $x)
- The retailer then sells Theo to the end consumer for $xxx plus a VAT of $3 totals to $33. The retailer pays $ane to the US government (Output VAT $3 reduced by the input VAT paid to Manufacturer $2). $1 paid represents the VAT on value addition fabricated in the cost toll of $x. ($thirty -$20)
Instance#2
Polo is a branded shirt in the US. The Charge per unit of VAT/ sales revenue enhancement in the Usa is x%.
Without Any Tax:
The Manufacturer of Polo spends $xx in raw material to manufacture the shirt, then the same is sold to a retailer for $xxx, and the retailer then finally sells the shirt to the end consumer for $xl.
With Sales Tax:
With the above example, the input cost for the Manufacturer volition be $twenty. The same would be sold to a retailer at the cost of $thirty, and the concluding price charged to consumers is $44 (Cost price 40 plus VAT @10 % is $four, and so totals to $44). In this consumer pays Sales revenue enhancement of $four. The retailer collects the tax from the consumer and pays it to the regime.
With VAT:
With the above case, the Manufacturer will pay $22 for raw material ($20 cost plus $2 VAT), the Manufacturer volition take $2 VAT paid as input credit. The same would be been sold to retailer past manufacturer at the price of $33 (Cost price + valued-added = $20+ $ten = $thirty plus VAT @10 % is $3 so totals to $33). Here the manufacturer pays $ane to the government ($3 output VAT – $2 input VAT) and the last price charged to consumer is $44 (Cost price + valued-added = $30+ $10 = $40 plus VAT @x % is $4 and so totals to $44). Here the retailer will pay $one to the regime ($4 output VAT – $3 input VAT). Though taxation is collected at various stages, the end consumer bears the full tax of $four.
So both in VAT/sales revenue enhancement, the tax corporeality remains the same, and it is borne only past the end consumer, but the preference is given to VAT since information technology is levied at every stage and every participant in the mechanism acts a taxation collector for the government and tax evasion is minimal in it. It is more than sophisticated than the sales taxation.
Advantages
- Revenue to the authorities under the VAT organisation volition be constant equally it is a consumption-based tax.
- It ensures better revenue enhancement compliance and tax evasion is reduced to the extent possible due to its take hold of upward result.
- Revenue earned by the regime via VAT is huge, as it is a low tax rate that is applied to the consumption of appurtenances.
- The VAT can be monitored and administered more than efficiently compared to other taxes prevailing.
- It is considered as a neutral taxation every bit it levied on all types of business.
- Its laws and rules are very transparent, and the tax is collected over various stages in smaller parts.
- This revenue enhancement is levied on the value-added on each stage and not on the total toll, and so in that location is no cascading event.
- In that location are the number of taxpayers A taxpayer is a person or a corporation who has to pay tax to the authorities based on their income, and in the technical sense, they are liable for, or subject to or obligated to pay tax to the government based on the country's tax laws. read more under this arrangement as information technology is levied on various stages, and all the terminate consumers pay the taxation on consumption irrespective of their income.
- The advantage to the government is that even for the goods which remaining in stock either with the benefactor or retailer, the government receives office of the tax.
Disadvantages
- The VAT is a picayune complicated as the identification of value-added in each stage is not an easy job.
- Its implementation across the billing system can be expensive.
- It can be considered effective just when the terminate consumers are enlightened of the tax organisation; otherwise, tax evasion is possible.
- The Manufacturer and distributors have to pay revenue enhancement in accelerate every bit the payment of taxation cannot be postponed till the goods are sold to terminate-users.
- End consumer doesn't gain or lose anything in the VAT organization as at that place is no credit for them.
- Since VAT is a taxation on the expense, this tax is regressive A regressive tax is the system of taxation where all citizens in the country are taxed at the aforementioned charge per unit without considering their income levels. As a result, a more than pregnant percentage of the income of the low-income grouping is charged every bit tax compared to the loftier-income group. read more in nature, and information technology affects the poor more than rich as they spend more proportion of their income.
Limitations
Equally VAT is a consumption-based taxation, information technology is an additional burden to the end consumers. This taxation is added to the toll of the products, and the finish consumer cannot avail of any credit or set off for the VAT paid by them. Therefore, information technology may affect the consumption pattern of the consumers, and demand & supply for the goods may vary. Though information technology contributes revenue to the government, it may reduce the purchasing ability of the consumer, and it can cause revenue loss to the economy as a whole. Tax will be considered every bit inefficient if the revenue lost because of the shift in demand is more than the acquirement gained by the regime past levying VAT. It is as well known every bit a deadweight loss When the 2 fundamental forces of Economy Supply and Demand are not balanced it leads to Deadweight loss. Deadweight loss could be calculated by drawing a graph of demand and supply. read more .
Decision
VAT is one of the nigh effective tax systems. In underdeveloped and developing countries, it makes meaning acquirement contributions to the government equally information technology is in the class of consumption tax Consumption Tax is a type of indirect tax you pay for using or "consuming" appurtenances and services. Also chosen Expenditure Tax, information technology includes sales, excise, tariffs, or some holding taxes. read more . In the VAT, tax evasion can be avoided, unlike sales tax The regime levies sales taxation on the consumption of various goods and services as the percentage added to the production and services from which the regime earns revenue and does the visitor'south welfare. In the United States, 38 unlike states have dissimilar taxes, from Alaska (1.76%) to Tennessee (ix.45%). read more , where it is easy to fiddle with. It brings a balanced revenue enhancement system in the country. It also ensures fairness and uniformity in the process.
Recommended Manufactures
This article has been a guide to what is Value Added Revenue enhancement and its definition. Here we provide you the formula to summate VAT forth with examples, advantages, and disadvantages. Yous can learn more than about fixed income from following articles –
- What are Payroll Taxes?
- Marginal Tax Rate Formula
- What is Revenue enhancement Lien?
- Examples of Indirect Taxes
Source: https://www.wallstreetmojo.com/value-added-tax-vat/
Posted by: smithgoidesseem.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can Florida Charge More Than 6% Sales Tax When Registering A Car Out Of State"
Post a Comment